The 7-Second Trick For A Patient's Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy - Concord


Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine - OrthoInfo - AAOS
The Buzz on Lumbar Spine Anatomy - SpineUniverse
This "tail of nerves "is called the cauda equina. The nerves that branch off of your lower spine and cauda equina control leg feelings and movement. This Is Cool and ligaments supply strength and stability to your lower back and enable you to flex forward, backward and rotate. The muscles that connect to your back spine consist of: This is the large, flat, broad triangular-shaped muscle. It starts at the bottom of the sixth thoracic vertebrae and the last three or 4 ribs and covers the width of your middle and lower back. Your" lats"help you use your arms to pull up your body weight, assist you breathe by raising your rib cage and assist you flex to the side. This three-muscle group moves your hip joint.
Your iliopsoas, one on each side of your body, flexes and supports your hip and lower back as you stroll, run and leave a chair. These muscles help you extend, side bend and turn. They likewise assist keep your upright body posture. Disks in the lumbar spinal column Intervertebral disks are the"shock absorber cushions"that sit between each vertebra. 5 disks are placed between the vertebrae of your back spinal column. In addition to functioning as a shock absorber, they help support your body's weight by bearing the load coming down your spinal column and enable motion between each vertebra. Ligaments of the back spine Ligaments in your back spinal column connect bone to bone to assist to keep your lumbar spine stable, permit smooth motion of your spinal column and help absorb the force of injury.
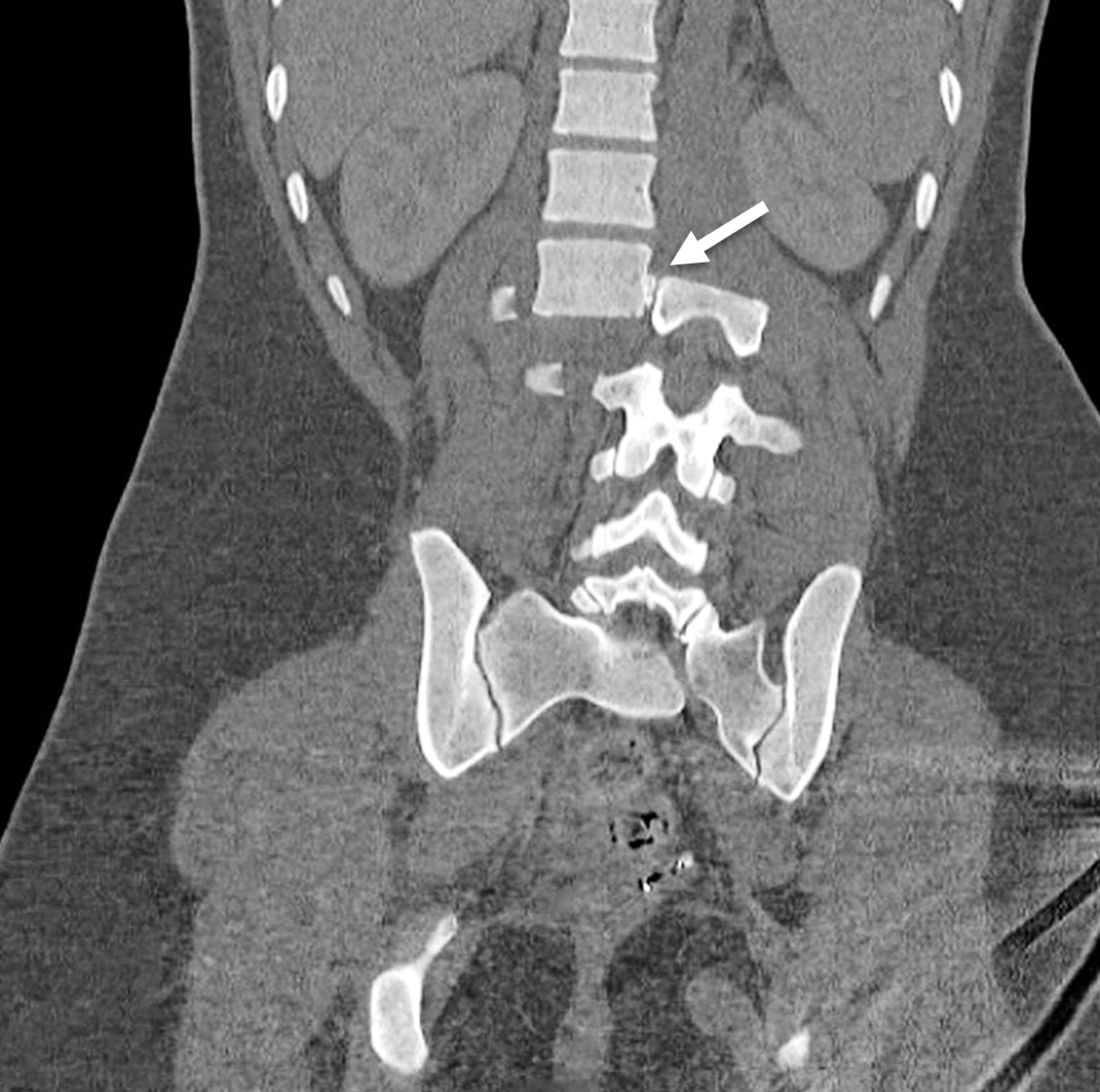
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Lumbar Spine (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
Back spine ligaments consist of: This ligament extends down the front of your back vertebrae. This ligament maintains the stability of your lumbar joints and limitations extension( backwards flexing of your back spinal column ). It limits flexion( forward bending )of your lumbar spine. The supraspinous ligament signs up with the ideas of the back of vertebra L1 to L3. Your interspinous ligament is a thin sheet of connecting tissue that
runs in between each vertebra, from the root of the spinous process to the suggestion. Both ligaments restrict flexion(forward flexing ). It brings messages in between your brain and muscles. The staying nerve roots, called the cauda equina, descend down the rest of your back canal. Nerves of the lumbar spinal column You have 5 sets of back spinal nerves, one that branches off from the.

